Introduction:
Journey through the vibrant history of École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), one of Europe’s most dynamic and innovative technical universities. Since its founding in 1853 as a private school, EPFL has evolved into a globally recognized research institution, pioneering advancements in science, engineering, and technology. Located in the heart of Europe, EPFL stands as a testament to Swiss excellence in education and research, bridging academic inquiry with real-world applications.
History:
EPFL began its journey with a focus on training engineers, gradually expanding its academic offerings and research scope. It became a federal institute in 1969, marking a pivotal moment that set the stage for its rapid growth and international reputation. Today, EPFL is known for its cutting-edge research facilities, interdisciplinary approach, and a strong emphasis on innovation and entrepreneurship. With its state-of-the-art campus on the shores of Lake Geneva, EPFL has become a melting pot of ideas, cultures, and scientific exploration.
The Latest Bing News on:
École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne Research
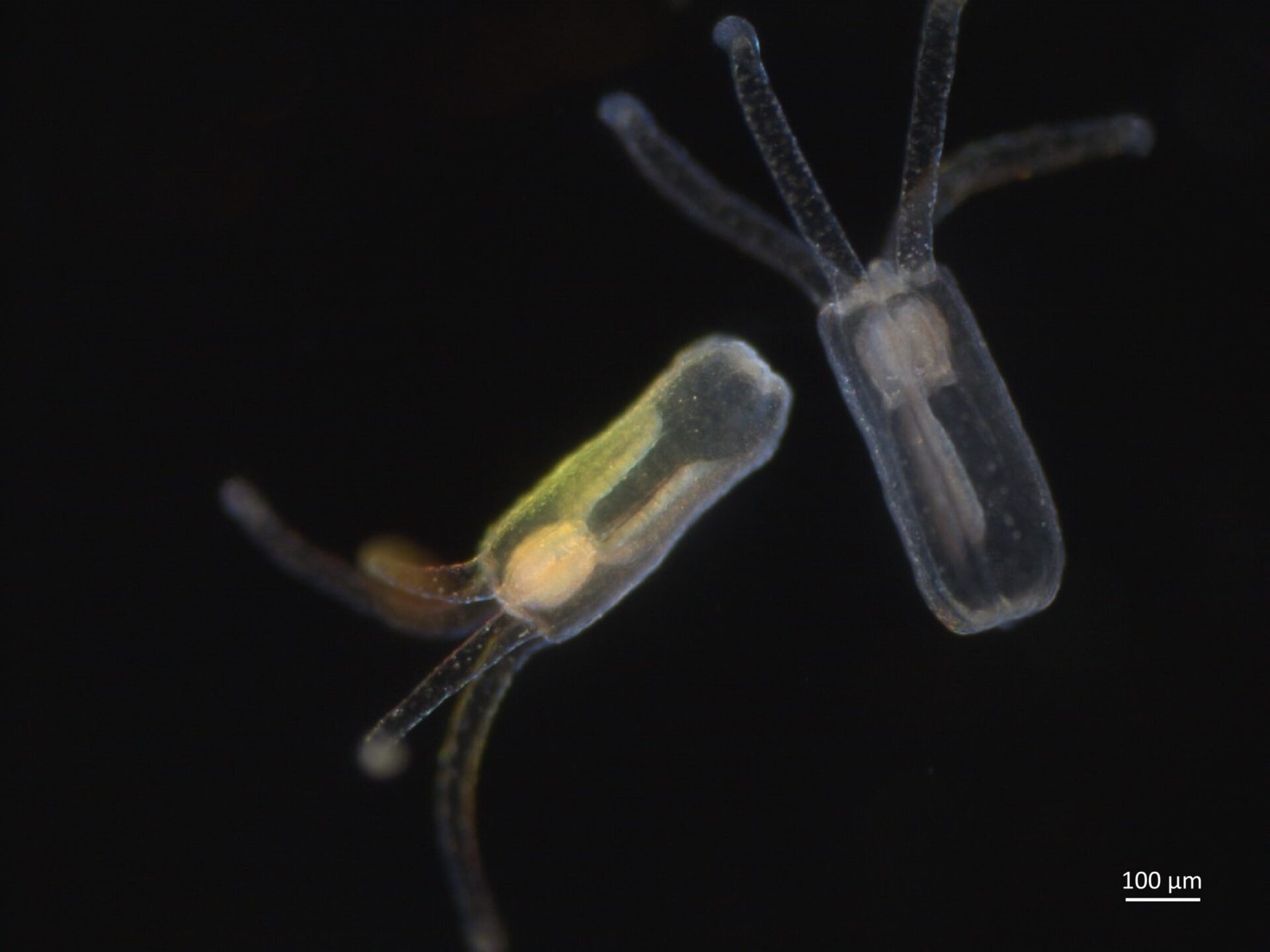
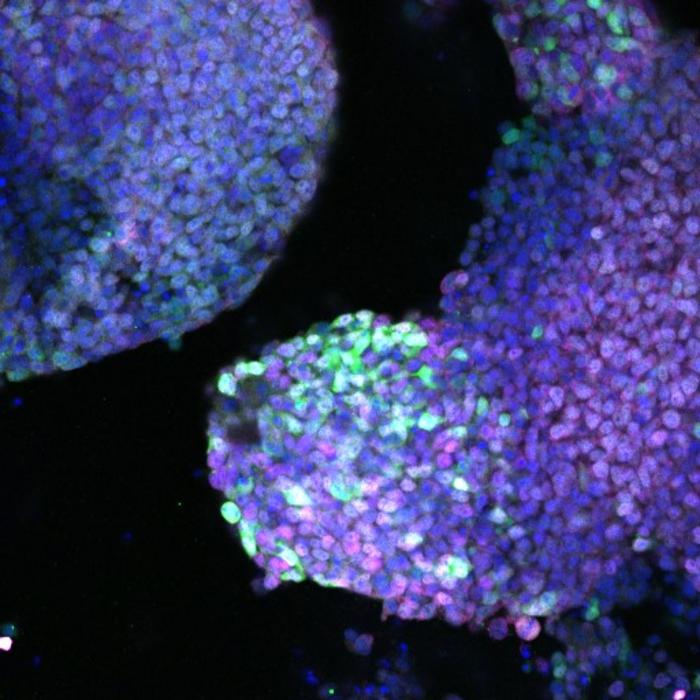
- Mini-colons advance colorectal cancer research
In a breakthrough for cancer research, scientists at EPFL have created lab-grown mini-colons that can accurately mimic the development of colorectal tumors, offering a powerful new tool for studying ...
- GCCA holds Innovandi Global Cement and Concrete Research Network Spring Week
GCCRN industrial chair and Cemex global research development vice president and Davide Zampini said “If we are to reach our goal of net zero concrete by 2050, then we cannot do so alone. We need to ...
- Best SEO keyword research tool of 2024
When it comes to SEO, Keyword research is probably among the most crucial aspects of the industry, and there is no doubt that there are hundreds of tools available online to do this. Now ...
- Modeling urban growth shows that cities develop in ways similar to cancerous tumors
A team of environmental engineers and city planners from University College London, the University of Sydney, and École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne ... Prior research has shown that ...
- Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne
The École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL ... Associated with several specialised research institutes, the two sister institutes form the ETH Domain, which is directly dependent ...
The Latest Bing News on:
École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne Discovery
- Novel lab-grown mini-colons can accurately mimic the development of colorectal tumors
In a breakthrough for cancer research, scientists at EPFL have created lab-grown mini-colons that can accurately mimic the development of colorectal tumors, offering a powerful new tool for studying ...
- Mini Colons Mimic Healthy, Tumor Tissue In Colorectal Cancer Development
The mini colons replicate both the physical structure and cellular diversity in the colon in both healthy and diseased states.
- Mini-colons advance colorectal cancer research
In a breakthrough for cancer research, scientists at EPFL have created lab-grown mini-colons that can accurately mimic the development of colorectal tumors, offering a powerful new tool for studying ...
- Energy Scientists Unravel the Mystery of Gold’s Glow
Discovery of effects behind photoluminescence in thin gold films could drive development of solar fuels and batteries ...
- Comprehensive model unravels quantum-mechanical effects behind photoluminescence in thin gold films
EPFL researchers have developed the first comprehensive model of the quantum-mechanical effects behind photoluminescence in thin gold films; a discovery that could drive the development of solar fuels ...
Top 20 Innovations:
- Blue Brain Project: A pioneering initiative in neuroscience to create a digital reconstruction of the brain.
- Flexible Electronics: Breakthroughs in the development of flexible and stretchable electronic circuits.
- Solar Energy Technologies: Significant advancements in photovoltaic systems and solar cells.
- Quantum Computing: Contributions to the field of quantum computing and quantum cryptography.
- Lab-on-a-Chip Technologies: Miniaturizing and integrating laboratory processes for rapid medical diagnostics.
- Humanoid Robotics: Development of advanced humanoid robots and artificial intelligence systems.
- Ultrafast Laser Technology: Innovations in laser technology, enabling ultrafast and high-precision applications.
- Biodegradable Batteries: Development of eco-friendly, biodegradable battery technologies.
- Biorobotics: Pioneering work in the integration of robotics with biological systems.
- 3D Printing Materials and Techniques: Advancements in additive manufacturing, especially in bioprinting and complex materials.
- Nanotechnology and Materials Science: Breakthroughs in nanoscale engineering and materials science.
- Wireless Communication Systems: Enhancements in wireless networking and communication technologies.
- Clean Water Technologies: Innovations in water purification and desalination technologies.
- Artificial Photosynthesis: Research in mimicking biological photosynthesis for energy production.
- Drones and UAV Technology: Development of cutting-edge drone technologies for various applications.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality: Contributions to VR and AR for educational and industrial uses.
- Environmental Monitoring Systems: Advanced technologies for environmental data collection and analysis.
- Biomedical Imaging Techniques: Innovations in medical imaging for improved diagnostics and treatment.
- Sustainable Urban Planning: Research in eco-friendly and sustainable urban development.
- Blockchain and Data Security: Advancements in blockchain technology and cybersecurity.
Top 20 Innovators:
- Patrick Aebischer: Former President of EPFL and a key figure in biomedical research.
- Adriano Aguzzi: Known for his groundbreaking work in the field of neurodegenerative diseases.
- Stéphanie Lacour: Renowned for her contributions to flexible electronics and neuroprosthetics.
- Demetri Psaltis: A leading figure in optical information processing and holography.
- Elison Matioli: He has made significant contributions in the field of energy, particularly in solar cells and LED technology.
- Henry Markram: Founder of the Blue Brain Project, a major initiative in computational neuroscience.
- Jürgen Brugger: Noted for his work in micro- and nanosystems technology.
- Selman Sakar: Renowned for his research in medical robotics and micro-nanorobots.
- Herbert Shea: His work in soft robotics and electroactive polymers is widely recognized.
- Nava Setter: Expert in ferroelectric materials and devices.
- Klaus Ensslin: Known for his research in quantum electronics.
- Auke Ijspeert: A leading researcher in biorobotics and computational neuroscience.
- Christophe Moser: His work in laser technology has had significant impacts.
- Tobias J. Kippenberg: Renowned for his contributions to optomechanics and nanophotonics.
- Michael Grätzel: Known for his invention of the dye-sensitized solar cell.
- Andreas Mortensen: His research in advanced composite materials is highly acclaimed.
- Jamie Paik: Notable for her work in robotics, particularly in origami robots and soft robotics.
- Stuart Parkin: A leader in spintronics and nanotechnology.
- Béla Suki: Known for his interdisciplinary work in lung mechanics and tissue engineering.
- Karl Deisseroth: A pioneer in optogenetics, though not primarily based at EPFL, his collaboration with the institute has been influential.
The École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, with its relentless pursuit of excellence and innovation, continues to redefine the landscape of scientific research and technological advancements. Through its interdisciplinary approach, commitment to addressing global challenges, and fostering of a vibrant academic community, EPFL stands not just as an educational institution but as a beacon of progress and a catalyst for change, inspiring the next generation of scientists, engineers, and leaders.
Created by ChatGPT (ChatGPT can make mistakes. Consider checking important information.)